

Catalogue# MCA-MBNL: Monoclonal Antibody to Mammalian Muscleblind Proteins.
The Immunogen: Muscleblind was originally isolated following studies of Drosophila, since inactivation of the muscleblind (mbl) gene in this species resulted in defects the development of muscles and the visual system (1). The Drosophila Muscleblind protein contains 4 so called Zn-CCCH Motifs (a.k.a. Cys3His or C3H motifs), members of the zinc finger family of nucleic acid binding motifs. The Zn-CCCH motifs are about 26 amino-acids long, co-ordinate one zinc ion and bind RNA. Human homologues of the single Drosophila muscleblind gene were discovered from cDNA and genomic sequencing, but were also discovered as a result of experiments aimed at finding proteins which bind to polynucleotide repeated sequences. Several important human diseases are associated with expansion of polynucleotide sequences, in most cases trinucleotide repeats. Myotonic dystrophy (DM1) is one of these diseases, and is associated with increases in the number of CTG repeats in the 3' UTR of the gene encoding myotonin (a.k.a. DM Kinase, DMK or myotonin-Protein Kinase), a ser/thr kinase expressed specifically in muscle. Normal humans have 5-37 tandem CTG repeats in this gene while those with myotonic dystrophy have from 50 to as many as 1,000 CTG repeats, with individuals with the most serious forms of the disease generally having the most repeats. Since the increased repeats were found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of the myotonin gene and so do not encode protein, it was puzzling as to how the increased number repeats caused the disease, especially since knock out of the myotonin gene has a relatively mild phenotype (2, 3). One theory is that the repeated sequences sequester important RNA binding and processing proteins and hence reduced the efficiency of RNA processing which would have a generally deleterious effect. To test this theory Miller et al. (4) looked for proteins that would bind specifically to the product of genomic CTG repeats in the 3' UTR, double stranded CUG RNA repeats. They found several which they named EXP proteins, for triplet repeat expansion dsRNA-binding proteins. These proteins were then identified as the mammalian homologues of the Drosophila Muscleblind protein. Mammalian genomes contain three muscleblind-like proteins, generally referred to as MBNL1, MBNL2 and MBNL3 (see below for other names), and all three were found to associate with long double stranded CUG RNA repeats. In situ hybridization studies in mouse show that all three genes are widely expressed especially in development and show significant overlap with myotonin expression (5). Recent studies show that transgenic knock out of MBNL1 in mice results in a phenotype similar to that of myotonic dystrophy, and also reduced efficiency of mRNA processing similar to those seen in this disease, both observations supporting the RNA sequestration theory (6). Although the exact function of Muscleblind proteins is not known, this and other evidence suggests that they have a role in splice site selection (6). We are happy to supply the excellent antibody generated by the research group who produced the research described in references 4 and 5.
We are OEM suppliers of this antibody- in this case researchers at the University of Florida generated this reagent, and we now manufacture it, have characterized it and generated the data presented on this page. This antibody is available from several other vendors, but we can supply it more cheaply and we can provide you with more detailed information on the properties of the antibody.
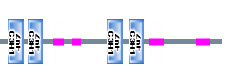
Diagram of Domain Structure: Generated from sequence of human MBLN1 with SMART program from EMBL in Heidleberg. Sequence is 371 amino acids long and is from the human MBNL1 sequence from Genbank. Boxes labelled Znf-C3H1 are the Zinc finger RNA binding motifs. Lilac boxes are regions of low protein sequence complexity, in this case regions rich in glutamine and/or alanine. Scale is number of amino acids;
![]()
Antibody characteristics: MCA-MBNL is a IgG1 class antibody with a k light chain and was raised against a preparation of recombinant human muscleblind protein. It reacts with all three Muscleblind proteins from human, mouse and rat. It is strong and clean on western blots and works well on frozen sections, cells in tissue culture and on formalin fixed histological sections.
Suggestions for use: Antibody is supplied as Integra CL-350 flask material, which is concentrated tissue culture supernatant. For immunofluorescence use MCA-MBNL diluted 1/50 to 1/250. For immunocytochemistry with ABC or other enzymatic methods use MCA-MBNL at dilutions of 1:1,000. For western blots try MCA-MBNL at dilutions of 1/1,000 to 1/5,000. Store at 4°C short term or -20°C long term. Antibody preparation contains 10mM sodium azide preservative (Press here to download a PDF of this information). Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
Limitations: This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis.
References:
1. Begemann G, Paricio N, Artero R, Kiss I, Perez-Alonso M. and Mlodzik M. Muscleblind, a gene required for photoreceptor differentiation in Drosophila, encodes novel nuclear Cys3His-type zinc-finger-containing proteins. Development 124:4321-4331 (1997).
2. Jansen G et al. Abnormal myotonic dystrophy protein kinase levels produce only mild myopathy in mice. Nat Genet. 13:316-324 (1996)
3. Reddy S et al. Mice lacking the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase develop a late onset progressive myopathy. Nat Genet. 13:325-335 (1996)
4. Miller JW, Urbinati CR, Teng-Umnuay P, Stenberg MG, Byrne BJ, Thornton CA and Swanson MS. Recruitment of human muscleblind proteins to (CUG)n expansions associated with myotonic dystrophy. EMBO J. 19:4439-4448 (2000).
5. Kanadia RN, Urbinati CR, Crusselle VJ, Luo D, Lee YJ, Harrison JK, Oh SP and Swanson MS. Developmental expression of mouse muscleblind genes Mbnl1, Mbnl2 and Mbnl3. Gene Expr. Patterns 3:459-462 (2003).
6. Kanadia RN, Johnstone KA, Mankodi A, Lungu C, Thornton CA, Esson D, Timmers AM, Hauswirth WW and Swanson MS. A muscleblind knockout model for myotonic dystrophy. Science 302:1978-1980 (2003).
OMIM Links: Muscle blind like protein 1 (MBNL1, a.k.a. MBNL, KIAA0428 and EXP) Press here, Muscleblind-like protein 2 (MBNL2, a.k.a. MBLL for Muscleblind-like protein like) Press here, Muscleblind like protein 3 (MBNL3, a.k.a. MBXL for Muscleblind-like protein X-linked) Press here.
Pfam Link: Press here
Availability and Price: Available for shipping now, $200 US per aliquot of 500 microliters of concentrated tissue culture derived material, enough for hundreds of experiments. For order form press here.
Use of Images or Text: The contents of this page are available for modification and reuse under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 and the GNU Free Documentation License, unversioned with no invariant sections, front-cover texts, or back-cover texts. These licences permit modification and reuse, even commercially, as long as authorship credit and a link to this page is given.